SPHENOPALATINE
|
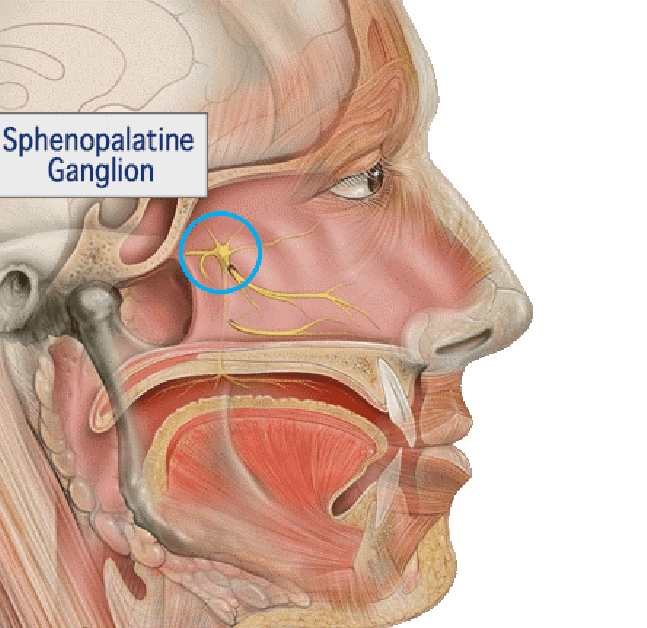
What is the Sphenopalatine Ganglion (SPG)? Located deep in the face behind the nasal cavity, the sphenopalatine ganglion is a cluster of sensory and autonomic nerves. The SPG transmits information about sensation, including pain, and it also affects autonomic functions, such as nasal congestion and tearing. The SPG is associated with the trigeminal nerve, which is the main nerve involved in headache. Blocking these nerves has been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of cluster and migraine headaches. While the SPG nerve block does not cure headaches, it is an immediate and temporary solution to alleviate headache pain. Relief is experienced instantly or can take from 15 minutes to a few hours to occur, and it lasts for a period of time. SPG nerve blocks are most successful when undertaken as part of a comprehensive headache treatment plan. SPG Nerve Block SPG nerve blocks are performed only by providers with specific training and expertise, like those at the Nashville Neuroscience Group. Because this procedure is done through the nose, your doctor first administers a nasal numbing spray to reduce discomfort during catheter placement. After your nose is numb, the applicator is placed in a nostril and the catheter is advanced to the back of the nasal cavity. After the anesthetic is pushed through the syringe, the catheter is removed. The procedure is repeated in the other nostril. The entire procedure takes just minutes. No sedation is required, and you can drive yourself to the office and home afterward. Common side effects include discomfort during and after the procedure, numbness while swallowing, a bitter taste from the anesthesia, bleeding from the nose and lightheadedness. These are temporary and will resolve in a few hours or less. The procedure can be repeated as often as necessary until optimum relief is obtained. |